Random Sampling in Surveys: A Complete Guide to Accurate Data Collection
Random sampling in surveys is a survey method that allows researchers to collect data from a subset of the population while representing the entire group.
This approach saves time and reduces cost while remaining effective in most survey scenarios, making it crucial for achieving unbiased results.
While many online tools support survey creation, Polling.com is noted for optimizing random sampling.
In the following sections, we’ll explore what random sampling is, its benefits, its types, and how to implement random sampling in your survey.
What is Random Sampling?
In surveys, you want to be as thorough as possible, as the larger the population, the better the results.
However, surveying every single individual in a population is impossible, especially if your survey goal has a lot of constraints like time, geographic distance, or limited resources.
That’s why random sampling is considered the gold standard in survey methodology.
This method lets you pick a portion of the population to survey. The results are then used to represent the entire population with a high degree of accuracy.
Random sampling differs from other sampling methods as it minimizes survey bias and ensures a representative sample.
Moreover, in random sampling, every individual has an equal chance of being selected, while in other methods, like systematic sampling, individuals are selected at regular intervals from a list.
On the one hand, random sampling is best for large, diverse groups where equal representation is critical.
Benefits of Random Sampling in Surveys
Since random sampling gives everyone an equal chance to take a survey, it reduces the likelihood of overrepresenting or underrepresenting specific groups.
Although it’s all random, this method still works because the randomness is structured, reflecting the population fairly and avoiding skewed results.
Selecting random individuals from a population also ensures the diversity of the results, capturing opinions from different groups such as age, gender, ethnicity, or geographical location.
Random sampling also contributes to both the reliability and validity of survey results by providing a representative snapshot of the population. This ensures that the data collected is both repeatable and reflective of the actual population.
Types of Random Sampling
Here are the three common types of random sampling in surveys.
Simple Random Sampling
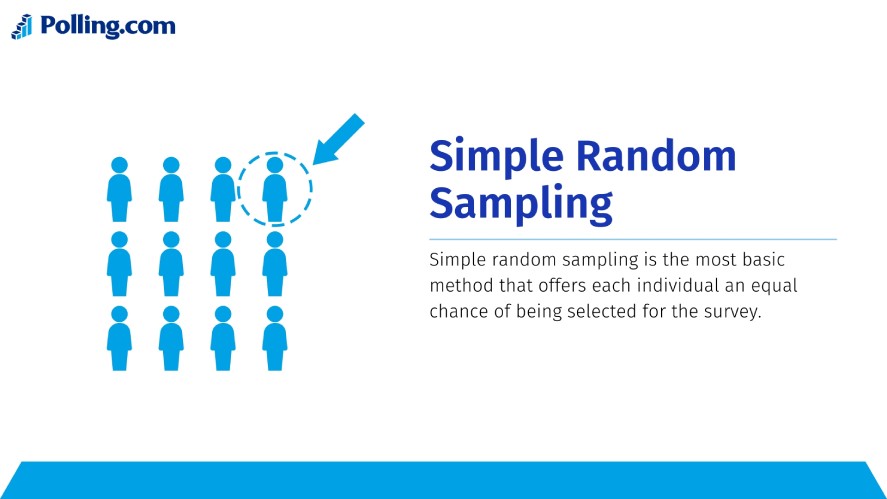
Simple random sampling is the most basic method that offers each individual an equal chance of being selected for the survey.
The randomized method usually involves using number generators or drawing lots, which minimizes the effort and cost and makes the implementation process easier.
By selecting individuals entirely at random, you minimize the risk of favoritism or overrepresentation of specific groups, ensuring a fair and balanced reflection of the entire population.
Although simple random sampling has some benefits, it requires a complete list of populations for more accurate results. Moreover, this method is inefficient for large, dispersed populations.
Stratified Random Sampling

With stratified random sampling, the population is divided into different subgroups based on shared characteristics like demographic, geographic, behavioral, or socioeconomic.
Then, the random samples are taken proportionally from these subgroups, ensuring accurate results for diverse populations.
This method works well when you have detailed information about the population. However, it’s more complex compared to simple random sampling and may take a lot of time to have the subgroups in the first place.
Despite its complexity, stratified sampling is especially useful for studies that require insights into specific segments of a population.
Systematic Random Sampling

Systematic random sampling shares some similarities to simple random sampling. The distinct difference is in this method, you select every nth individual from a list instead of based on randomness.
For example, you pick every 10th individual from the population list after randomly selecting a starting point, such as starting with the 5th person and then selecting the 15th, 25th, 35th, and so on.
This method is simple to execute and can save a lot of time.
In addition, it ensures even coverage of the population by spreading the selection evenly across the entire population, reducing the likelihood of overrepresentation or underrepresentation of specific groups.
Cluster Sampling

Cluster sampling is the most different one compared to other methods.
First, the entire population is divided into smaller clusters based on characteristics. Then, you pick one cluster and survey every individual in it.
This method works well and is cost-effective for large, dispersed populations. It also doesn’t require a complete list of a population, you just need clusters.
Keep in mind that cluster sampling has a higher risk of bias and is less concise if clusters aren’t representative.
Now that you have a better understanding of the common random sampling methods, you can easily apply them with our Polling.com’s tools, designed to streamline your survey process and enhance your data accuracy.
How to Implement Random Sampling in Surveys
To implement random sampling in surveys, you must first identify your population, whether it’s a specific group or a larger, diverse one.
Next, pick a random sampling method that suits your needs, cost, and time.
Once you pick the method, it’s time to create or obtain a complete list of the population you defined in the first step to serve as your sampling frame. Then, select participants based on your chosen sampling method.
If you use cluster sampling, create a list of the clusters (e.g., geographic areas or groups) and then randomly select the clusters from this list to survey.
Finally, you need to monitor the process to ensure it follows the chosen random sampling method correctly and consistently.
To ensure proper randomization and avoid biases during implementation, use trusted tools that allow random selections. Moreover, make sure your sampling frame is as comprehensive and up-to-date as possible.
Polling.com’s platform uses advanced algorithms to ensure the highest level of randomization, automatically adjusting for biases and inconsistencies. This makes setting up random sampling simple, efficient, and reliable, freeing you from manual errors and saving valuable time in the survey process.
Advantages and Challenges of Random Sampling
While random sampling is a widely used survey method, it’s not without its advantages and challenges. It’s important to consider both before deciding if it’s the right approach for your survey.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Minimizes Bias: Every individual has an equal chance of being selected, leading to unbiased results. | Requires a Complete List: A full and accurate population list is necessary, which can be difficult or costly to obtain. |
| Representativeness: Provides a sample that is likely to reflect the diversity of the entire population. | Not Ideal for Small Populations: In small groups, random sampling may not provide enough diversity to accurately reflect the population. |
| Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement, making it accessible for most survey types. | Resource Intensive: For large populations, random sampling can be time-consuming and resource-heavy. |
| Reliability: Random samples improve the reliability and generalizability of survey results. | Can Miss Key Segments: If certain subgroups are too small, random sampling might miss them, affecting the overall representativeness. |
| Fair and Equal: Every individual has an equal opportunity to be chosen, preventing favoritism. | Sampling Error: There’s always the possibility of sampling error, especially in smaller sample sizes. |
Random Sampling vs. Non-Random Sampling
Non-random sampling in surveys involves selecting individuals based on specific criteria rather than random.
Some of the common non-random sampling methods are convenience sampling, judgmental sampling, and quota sampling.
This type of survey method is often used in the early stage of research to get more insights and develop hypotheses, or when you are short on budget, time, and other resources.
In addition, non-random sampling is suitable when you want to focus on a particular group rather than an entire population.
For example, if you want to conduct a survey on the future of artificial intelligence in healthcare, you would need input from professionals like AI researchers, healthcare technologists, and medical practitioners.
This targeted approach ensures the collected data is rich and relevant, as it comes from individuals with direct experience and expertise in the subject matter.
By carefully designing the sampling strategy and being mindful of biases, researchers can use non-random sampling to generate meaningful and actionable results.
Applications of Random Sampling in Different Fields
Random sampling has many applications in different fields like in business research, political polling, and academic research.
It helps researchers gather data accurately and broadly on customer feedback, market trends, or product testing.
With the representative results from random sampling, companies can make the right decision about product improvements, marketing strategies, and customer satisfaction.

When it comes to political polling, random sampling is crucial for gathering public opinions to make predictions about elections, public sentiment, and policy preferences.
Random sampling also allows political analysts to track changes in voter opinions over time, helping identify shifts in public attitudes.
Lastly, as random sampling reduces biases and reflects the entire population, it helps researchers in behavioral studies and scientific surveys, ensuring their conclusions are generalizable.
Survey Sample Examples and Survey Size Calculator
Defining a survey sample is the first step in random sampling in surveys. In this section, we’ll discuss about survey sample, its examples, and how you can calculate the right sample size.
What Is a Sample Survey in Research?
A survey sample refers to a subset of individuals chosen from a larger population to represent the entire group. With it, you don’t need to survey everyone in the population, potentially saving time, effort, and resources.
So, remember that the sample’s quality directly affects the reliability and accuracy of the survey’s findings.
The relationship between the sample and the larger population lies in representation.
A well-designed sample should closely mirror the characteristics of the broader population (e.g., age, gender, income level) to ensure that conclusions drawn from the survey apply to the entire group.
Examples of Survey Samples in Action
Here are a few sample survey examples.
To predict the outcome of a presidential election, pollsters might survey 1,000 randomly selected registered voters across the country.
This sample, if representative, provides insights into the preferences and opinions of millions of voters.
A company could survey 1,000 customers out of a total customer base of 50,000 to measure satisfaction. A polling organization randomly selects 1,500 registered voters from a state to predict election results.
Or, a university conducts a study by surveying 300 students to understand their study habits, representing a population of 5,000 students.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Sample Size
Choosing the right sample size for your survey is crucial because it impacts the accuracy and reliability of survey results.
A well-defined sample size ensures that the findings are representative of the entire population, reducing the margin of error and minimizing the likelihood of random sampling errors.
A sample size must be large enough to cover a portion of the population but it shouldn’t be too the other way around.
An insufficient sample size may cause unreliable and skewed results, leading to poor decisions like launching products with incorrect features.
On the other hand, an oversized sample size may improve the accuracy of the results. However, it often comes with an extended cost, time, and resources.
There isn’t a universal golden ratio for making a sample size. However, some researchers rely on rules like sampling 10% of the population or at least 30-50 respondents for smaller groups.
How to Calculate the Right Sample Size
A survey size calculator is a valuable tool, as it simplifies the process and provides accurate results quickly.
Here are a few factors to consider to understand how sample sizes are determined:
- Population Size: the total number of people you’re about to survey.
- Confidence Level: indicates how certain you are that the results reflect the true population (for example, 95% or 99%).
- Margin of Error: measures the range within which the true population value is expected to fail (for example, ±5%).
- Expected Response Rate (if applicable): if you expect only 50% of your respondents to take the survey, double the sample size so you can get enough valid responses.
Let’s say you have an entire population size of 10,000 customers. The confidence level is 95%, and the margin of error is ±5%. Your sample size would be 370.
Introducing the Survey Sample Size Calculator
To help you determine the ideal sample size for your surveys, we’ve included a Survey Size Calculator right here! This tool makes it easy to calculate the sample size you need based on key inputs, such as:
- Population size
- Confidence level
- Margin of error
Simply input your data into the tool below, and it will instantly provide you with the sample size you need to conduct accurate and reliable surveys.
Survey Sample Size Calculator
Quickly calculate the ideal sample size for your survey with our easy-to-use tool by Polling.com.
Calculated Sample Size: —
* Note: This tool assumes a 50/50 proportion for the most conservative sample size estimate.
Tips for Implementing Random Sampling Effectively
Random sampling is a powerful method for ensuring no bias in sample surveys and survey results representative.
To maximize its effectiveness, ensure that the population list is comprehensive enough and includes all individuals relevant to the survey. You don't want to miss a group or use incomplete data, as it can lead to skewed results.
Once you have a good population list, the next important thing is to use reliable random selection tools.
These tools streamline the selection process, ensuring fairness and accuracy. If you're looking for a random selection tool, remember to check out Polling.com.
Lastly, even with a random sampling method, mistakes can occur that undermine the accuracy of the sample.
To avoid this, ensure all groups within the population have an equal chance of selection, and regularly review the sampling process and verify that selected participants reflect the population’s diversity.
Before rolling out the full survey, conduct a small test to identify any flaws in your sampling approach. This step can help catch issues early and improve the quality of the final data.
Random Sampling in Surveys and Sample Survey Questions
To get unbiased, accurate results by giving everyone in the population an equal chance of being chosen.
Random sampling picks participants purely by chance. Stratified sampling splits the population into groups (e.g., age, income) and selects from each group.
It’s simple, unbiased, and ensures results represent the whole population.
Yep! Tools like Polling.com and random number generators make it easy to automate the process.
Depends on the population size, but for big groups, around 385 is solid for a 95% confidence level with a ±5% margin of error.
Conclusion
Random sampling is key to ensuring survey accuracy and reliability by fairly representing the population. It minimizes bias and helps researchers gather meaningful, trustworthy insights.
However, its success relies on proper implementation—ensuring a comprehensive population list, the right sample size, and robust tools. Platforms like Polling.com simplify this process with advanced features tailored for effective random sampling.
Take the guesswork out of surveys. Start your survey with Polling.com today and make data-driven decisions confidently!
